How to deploy Molmo 7B-D-0924 in the Cloud?

A vision-language model created by the Allen Institute for AI, Molmo 7B D 0924 is a member of the Molmo family. Molmo AI is an powerful, open-source multimodal AI models that's freely available to everyone. It stands apart from other multimodal models of a comparable size due to its state-of-the-art performance and complete open-source nature.
Using OpenAI CLIP as its vision backbone, this Qwen2-7B-based model can easily perform between GPT-4V and GPT-4o on academic benchmarks and human evaluations. Additionally, it is the force behind the Molmo demo. The Molmo 7B D 0924 is a model that's well worth looking at thanks to its amazing features.
Evaluations
| Model | Average Score on 11 Academic Benchmarks | Human Preference Elo Rating |
|---|---|---|
| Molmo 72B | 81.2 | 1077 |
| Molmo 7B-D (this model) | 77.3 | 1056 |
| Molmo 7B-O | 74.6 | 1051 |
| MolmoE 1B | 68.6 | 1032 |
| GPT-4o | 78.5 | 1079 |
| GPT-4V | 71.1 | 1041 |
| Gemini 1.5 Pro | 78.3 | 1074 |
| Gemini 1.5 Flash | 75.1 | 1054 |
| Claude 3.5 Sonnet | 76.7 | 1069 |
| Claude 3 Opus | 66.4 | 971 |
| Claude 3 Haiku | 65.3 | 999 |
| Qwen VL2 72B | 79.4 | 1037 |
| Qwen VL2 7B | 73.7 | 1025 |
| Intern VL2 LLAMA 76B | 77.1 | 1018 |
| Intern VL2 8B | 69.4 | 953 |
| Pixtral 12B | 69.5 | 1016 |
| Phi3.5-Vision 4B | 59.7 | 982 |
| PaliGemma 3B | 50.0 | 937 |
| LLAVA OneVision 72B | 76.6 | 1051 |
| LLAVA OneVision 7B | 72.0 | 1024 |
| Cambrian-1 34B | 66.8 | 953 |
| Cambrian-1 8B | 63.4 | 952 |
| xGen - MM - Interleave 4B | 59.5 | 979 |
| LLAVA-1.5 13B | 43.9 | 960 |
| LLAVA-1.5 7B | 40.7 | 951 |
With its ability to enable rich interactions with both real-world and virtual contexts, Molmo AI opens the door for a new class of applications. It scores admirably on human evaluation and academic criteria, with a capability that lies between GPT-4V and GPT-4o. This checkpoint serves as a sneak peek at the next Molmo model release.
PixMo, a dataset including one million carefully selected image-text pairs, is used to train Molmo models. Being totally open-source, it achieves state-of-the-art performance among multimodal models of comparable scale. All of the Molmo family's models are available here.
Features of Molmo AI
- Learning perceives
- Smaller Size
- Multimodals Models
- Top Performance
- Easy Integration
- Open-Source
Model Inputs and Outputs
Inputs
- Images: One image can be processed by the model at a time. The image can be passed as a PIL Image object.
- Text: In order to characterize the given image, the model receives a text prompt as input.
Outputs
- Text: The output of the model is text that describes the supplied image. A text string is the result.
In this blog, you'll learn:
- About Molmo 7B-D-0924 model
- Setup GPU-powered Virtual Machine offered by NodeShift
- Run Molmo 7B-D-0924 Model in the NodeShift Cloud.
Step-by-Step Process to deploy Molmo 7B-D-0924 Model in the Cloud
For the purpose of this tutorial, we will use a GPU-powered Virtual Machine offered by NodeShift; however, you can replicate the same steps with any other cloud provider of your choice. NodeShift provides the most affordable Virtual Machines at a scale that meets GDPR, SOC2, and ISO27001 requirements.
Step 1: Sign Up and Set Up a NodeShift Cloud Account
Visit the NodeShift Platform and create an account. Once you've signed up, log into your account.
Follow the account setup process and provide the necessary details and information.
Step 2: Create a GPU Node (Virtual Machine)
GPU Nodes are NodeShift's GPU Virtual Machines, on-demand resources equipped with diverse GPUs ranging from H100s to A100s. These GPU-powered VMs provide enhanced environmental control, allowing configuration adjustments for GPUs, CPUs, RAM, and Storage based on specific requirements.
Navigate to the menu on the left side. Select the GPU Nodes option, create a GPU Node in the Dashboard, click the Create GPU Node button, and create your first Virtual Machine deployment.
Step 3: Select a Model, Region, and Storage
In the "GPU Nodes" tab, select a GPU Model and Storage according to your needs and the geographical region where you want to launch your model.
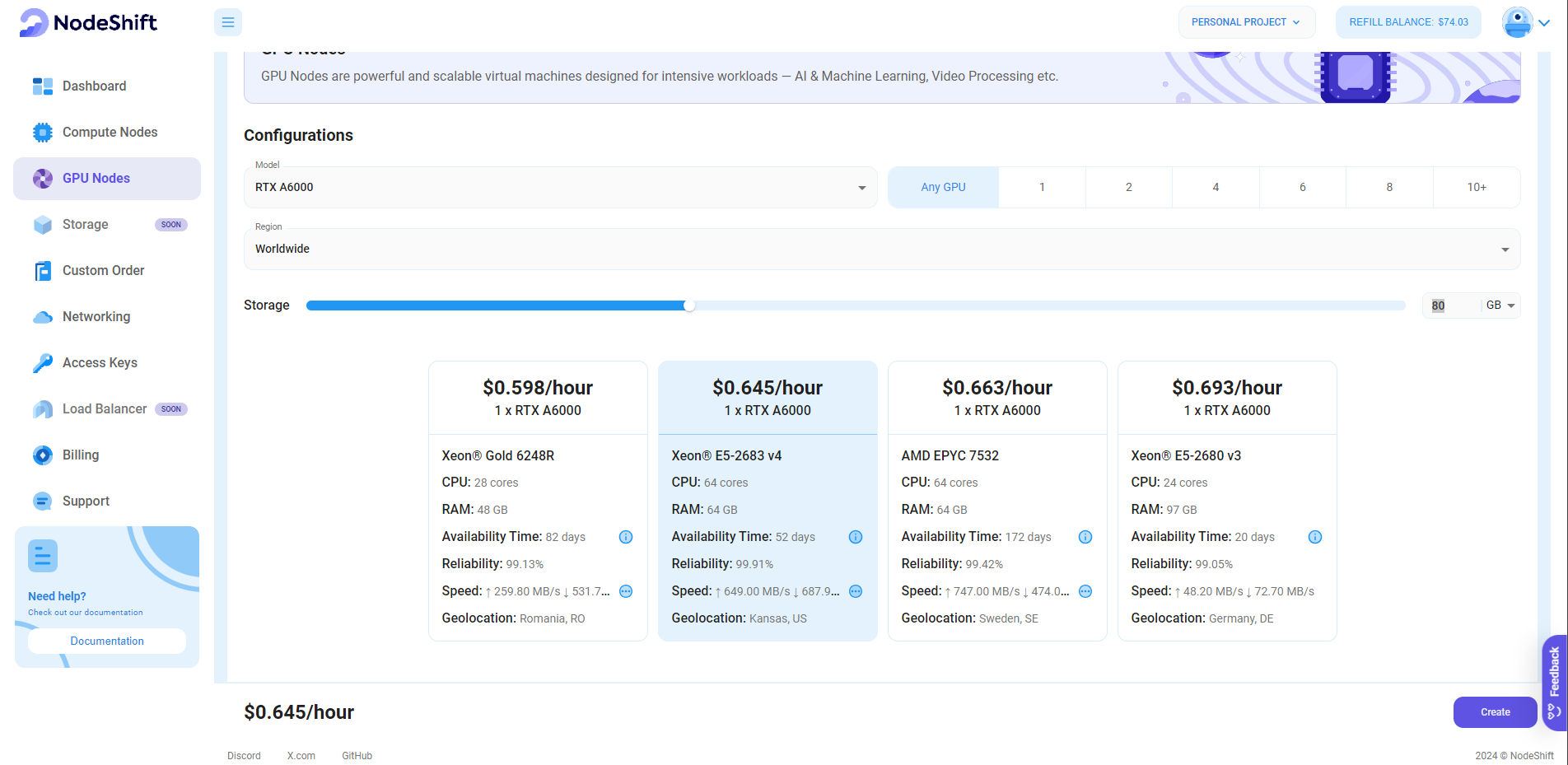
We will use 1x RTX A6000 GPU for this tutorial to achieve the fastest performance. However, you can choose a more affordable GPU with less VRAM if that better suits your requirements.
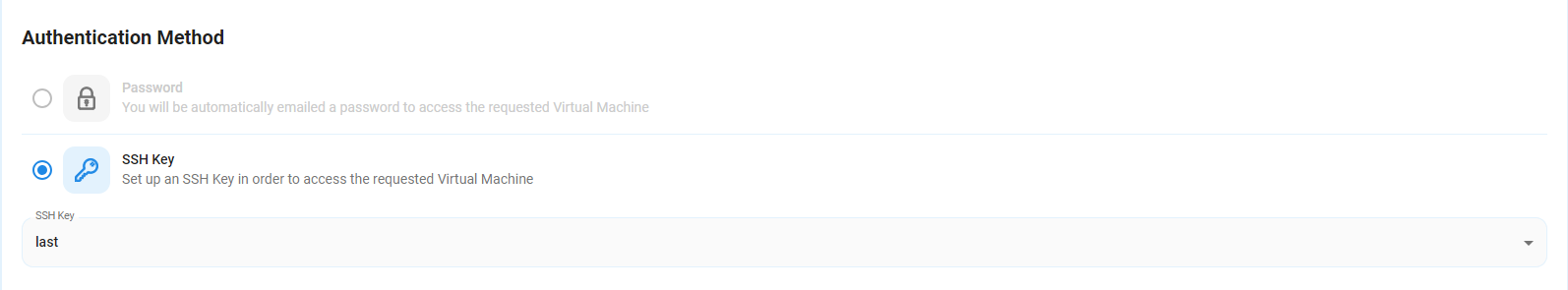
Step 4: Select Authentication Method
There are two authentication methods available: Password and SSH Key. SSH keys are a more secure option. To create them, please refer to our official documentation.
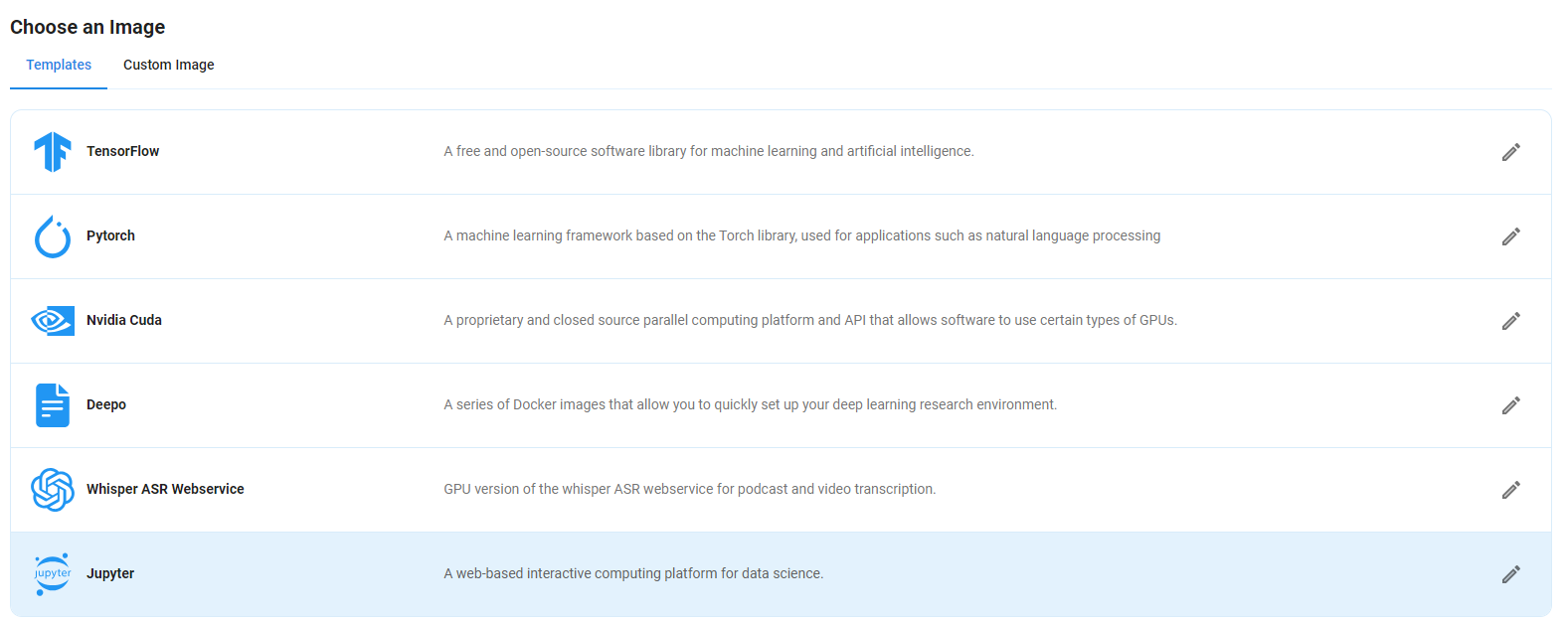
Step 5: Choose an Image
Next, you will need to choose an image for your Virtual Machine. We will deploy the Molmo 7B-D-0924 Model on a Jupyter Virtual Machine. This open-source platform will allow you to install and run the Molmo 7B-D-0924 Model on your GPU node. By running this model on a Jupyter Notebook, we avoid using the terminal, simplifying the process and reducing the setup time. This allows you to configure the model in just a few steps and minutes.
Note: NodeShift provides multiple image template options, such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, NVIDIA CUDA, Deepo, Whisper ASR Webservice, and Jupyter Notebook. With these options, you don’t need to install additional libraries or packages to run Jupyter Notebook. You can start Jupyter Notebook in just a few simple clicks.
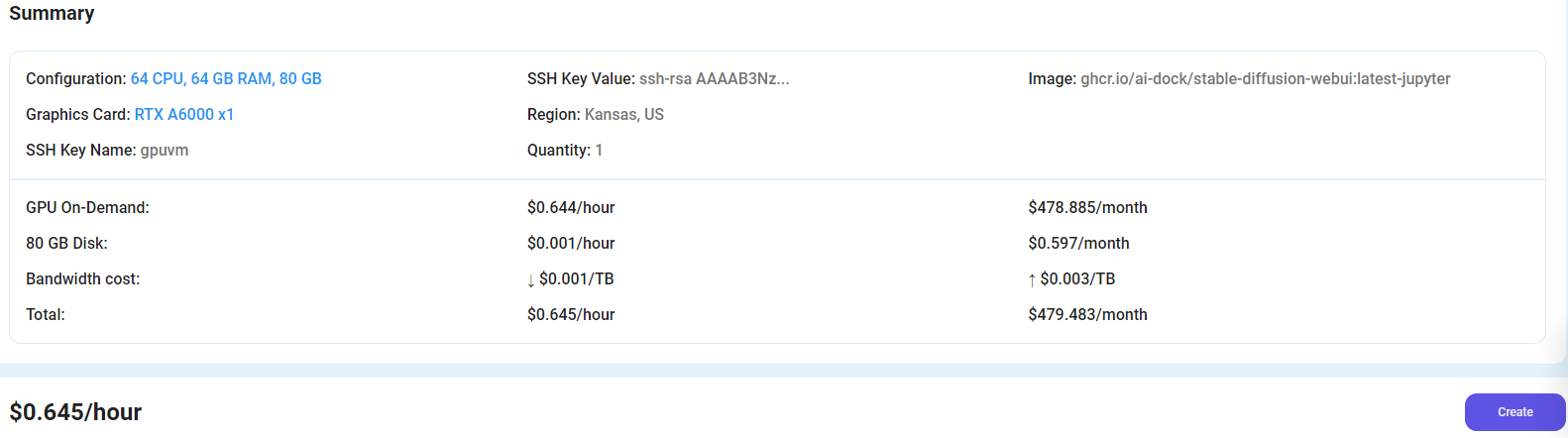
After choosing the image, click the 'Create' button, and your Virtual Machine will be deployed.
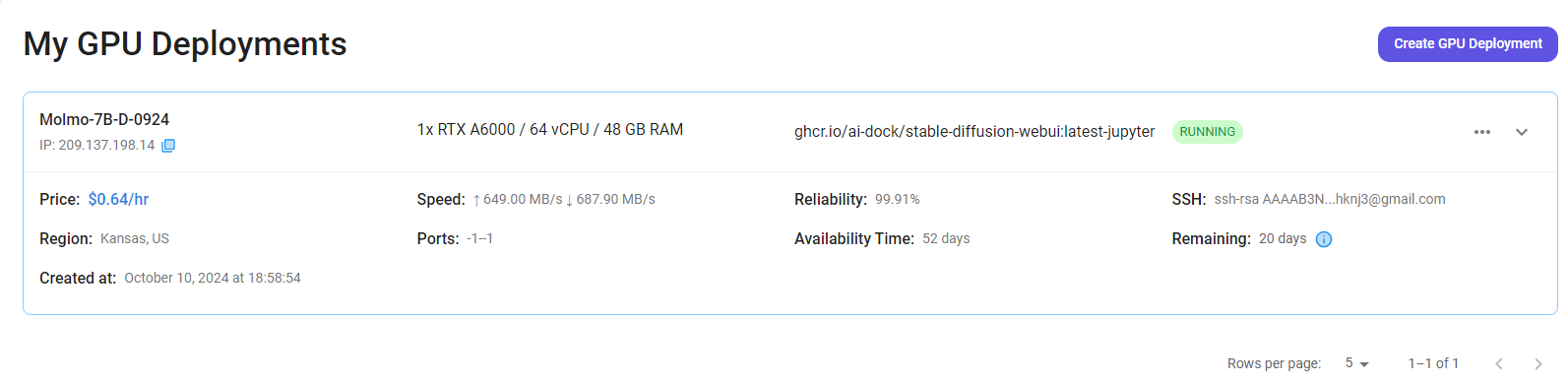
Step 6: Virtual Machine Successfully Deployed
You will get visual confirmation that your node is up and running.
Step 7: Connect to Jupyter Notebook
Once your GPU VM deployment is successfully created and has reached the 'RUNNING' status, you can navigate to the page of your GPU Deployment Instance. Then, click the 'Connect' Button in the top right corner.
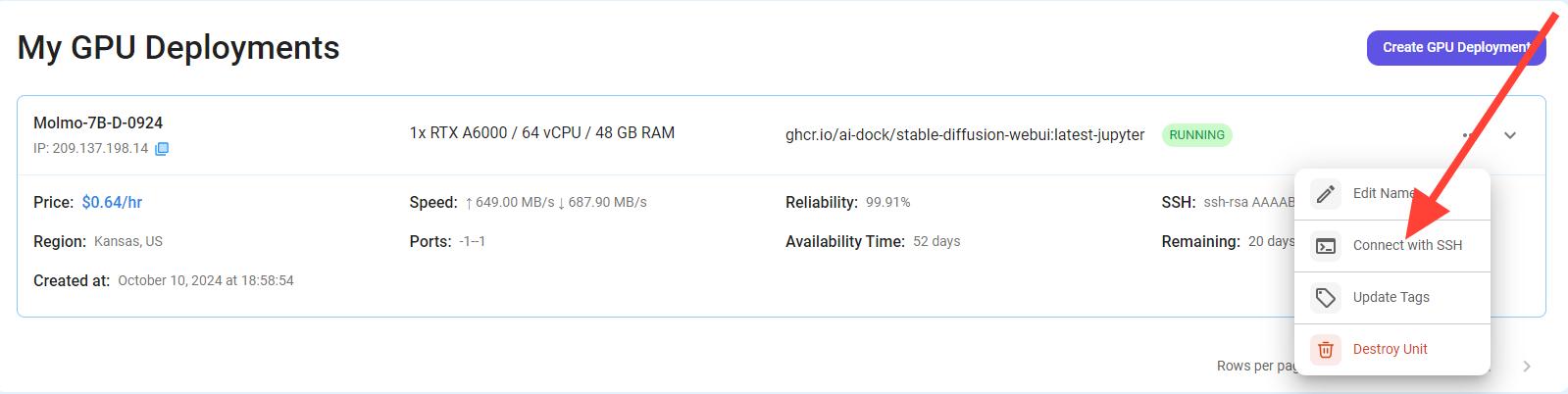
After clicking the 'Connect' button, you can view the Jupyter Notebook.
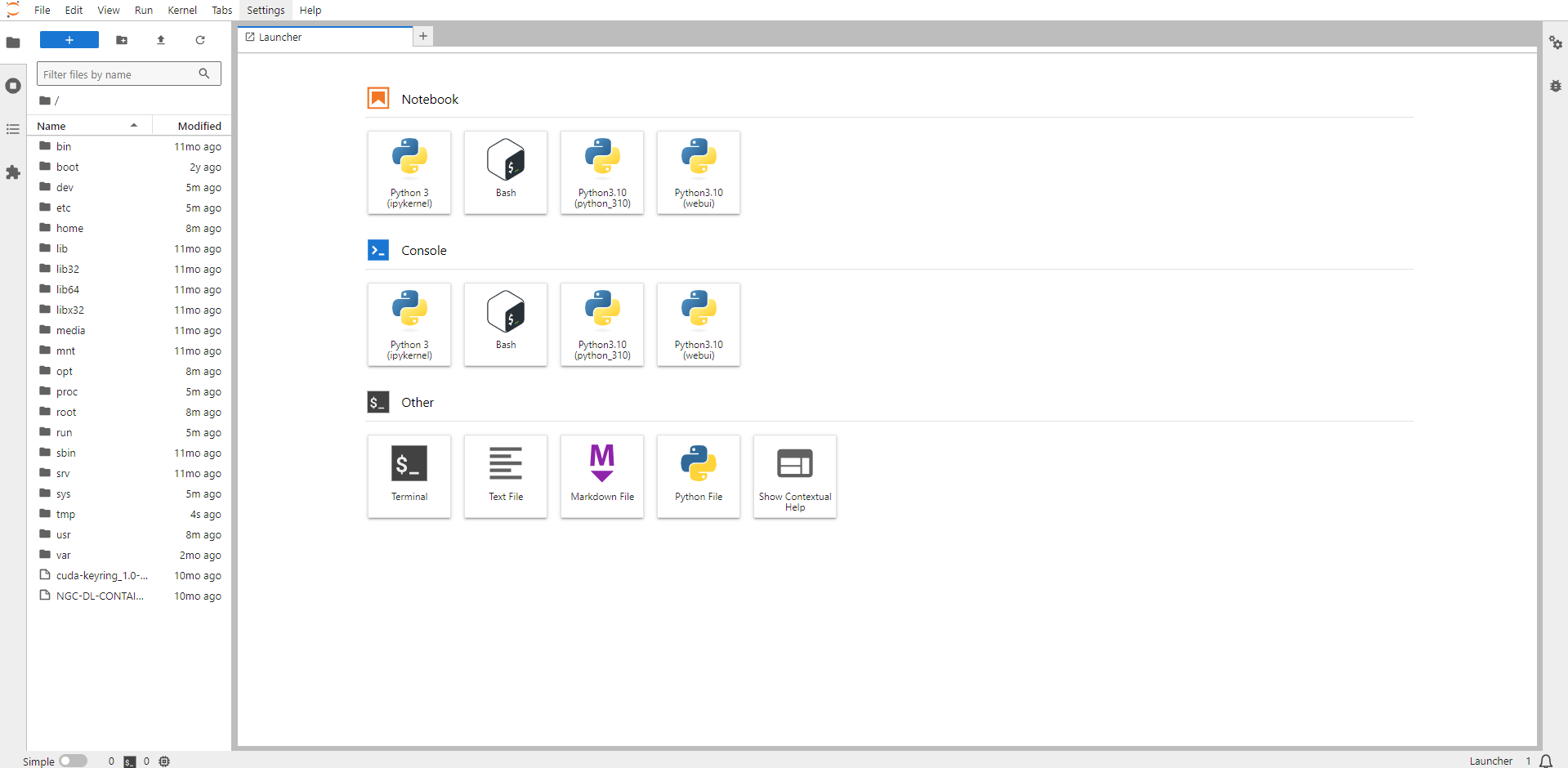
Now open Python 3(pykernel) Notebook.
Next, If you want to check the GPU details, run the command in the Jupyter Notebook cell:
!nvidia-smi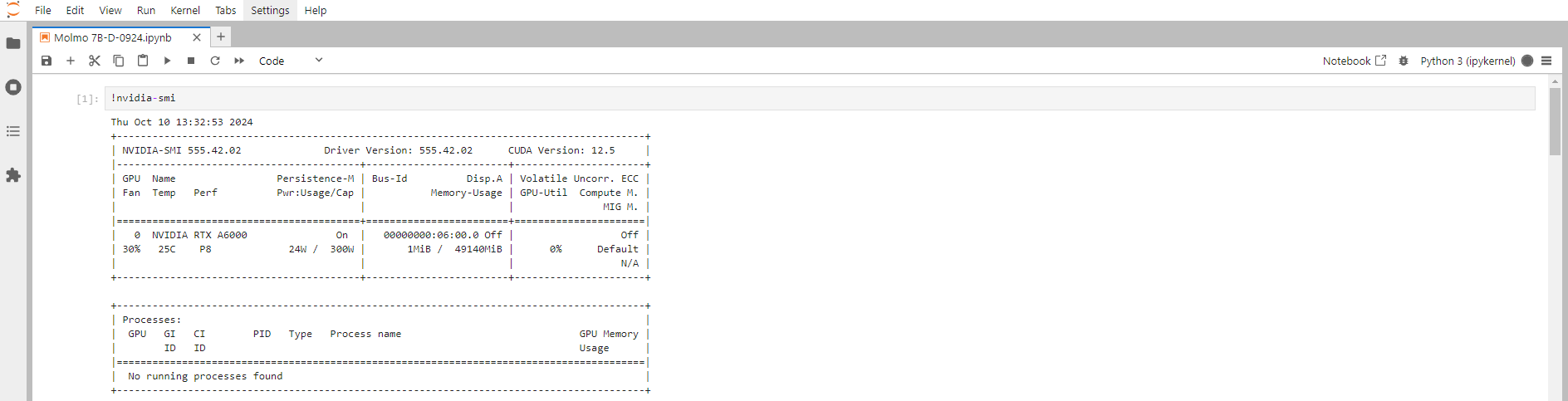
Step 8: Install the Torch Library
Torch is an open-source machine learning library, a scientific computing framework, and a scripting language based on Lua. It provides LuaJIT interfaces to deep learning algorithms implemented in C.
Torch was designed with performance in mind, leveraging highly optimized libraries like CUDA, BLAS, and LAPACK for numerical computations.
Run the following command in the Jupyter Notebook cell to install the Torch Library:
pip install torch
Step 9: Install Transformers from GitHub
Run the following command in the Jupyter Notebook cell to install the Transformers:
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformersTransformers provide APIs and tools to download and efficiently train pre-trained models.
Step 10: Install Accelerate from GitHub
Run the following command in the Jupyter Notebook cell to install the Accelerate:
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerateAccelerate is a library that enables the same PyTorch code to be run across any distributed configuration by adding just four lines of code.
Step 11: Install Huggingface Hub
Run the following command in the Jupyter Notebook cell to install the Huggingface Hub:
pip install huggingface_hubHugging Face Hub is the go-to place for sharing machine learning models, demos, datasets, and metrics. huggingface_hub library helps you interact with the Hub without leaving your development environment.
Step 12: Install Torchvision
Run the following command in the Jupyter Notebook cell to install the Torchvision:
pip install TorchvisionTorchvision is a library for Computer Vision that goes hand in hand with PyTorch. It has utilities for efficient Image and Video transformations, some commonly used pre-trained models, and some datasets ( torchvision does not come bundled with PyTorch, you will have to install it separately. )
Step 13: Install Sentencepiece
Run the following command in the Jupyter Notebook cell to install the Sentencepiece:
pip install SentencepieceSentencePiece is a language-independent subword tokenizer and detokenizer designed for neural text processing, including neural machine translation (NMT). It enables the creation of end-to-end systems that can handle raw sentences without the need for pre-tokenization.
Step 14: Install Bitsandbytes
Run the following command in the Jupyter Notebook cell to install the Bitsandbytes:
pip install BitsandbytesBitsandbytes is a Python library that provides 8-bit optimizers and quantization utilities for accelerating model training and inference in deep learning. It enables the use of lower precision (8-bit) arithmetic to reduce memory usage and improve computational efficiency, making it especially useful for large models.
Step 15: Install Einops
Run the following command in the Jupyter Notebook cell to install the Einops:
pip install EinopsEinops (Einstein Operations) is a powerful library for tensor manipulation, offering a more readable and efficient way to perform operations on tensors.
Step 16: Run the Molmo 7B-D-0924 code
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoProcessor, GenerationConfig
from PIL import Image
import requests
# load the processor
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(
'allenai/Molmo-7B-D-0924',
trust_remote_code=True,
torch_dtype='auto',
device_map='auto'
)
# load the model
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
'allenai/Molmo-7B-D-0924',
trust_remote_code=True,
torch_dtype='auto',
device_map='auto'
)
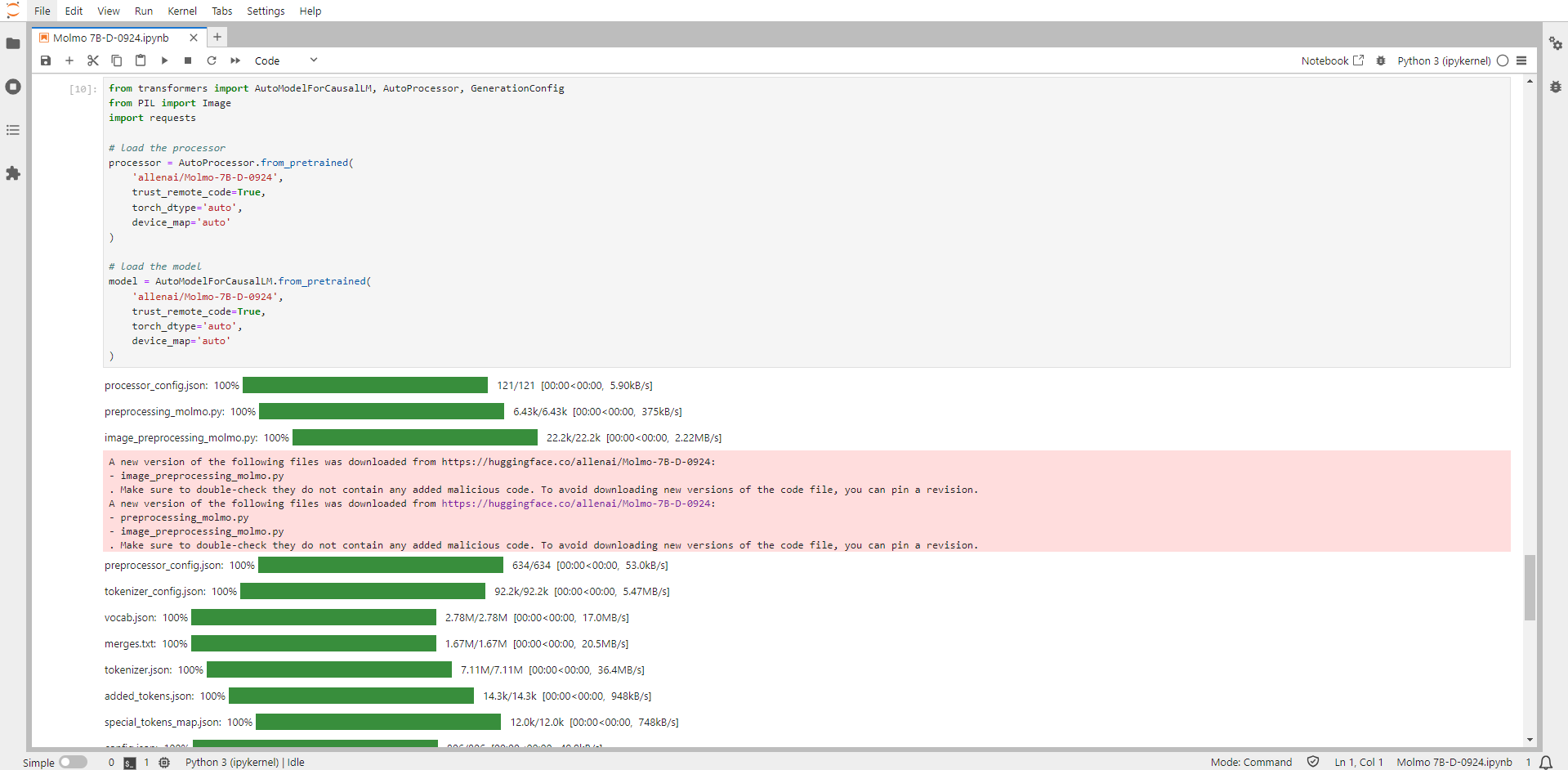
Step 17: Run the Prompt and Print the Output
Example 1:
# process the image and text
inputs = processor.process(
images=[Image.open(requests.get("https://picsum.photos/id/237/536/354", stream=True).raw)],
text="Describe this image."
)
# move inputs to the correct device and make a batch of size 1
inputs = {k: v.to(model.device).unsqueeze(0) for k, v in inputs.items()}
# generate output; maximum 200 new tokens; stop generation when <|endoftext|> is generated
output = model.generate_from_batch(
inputs,
GenerationConfig(max_new_tokens=200, stop_strings="<|endoftext|>"),
tokenizer=processor.tokenizer
)
# only get generated tokens; decode them to text
generated_tokens = output[0,inputs['input_ids'].size(1):]
generated_text = processor.tokenizer.decode(generated_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True)
# print the generated text
print(generated_text)
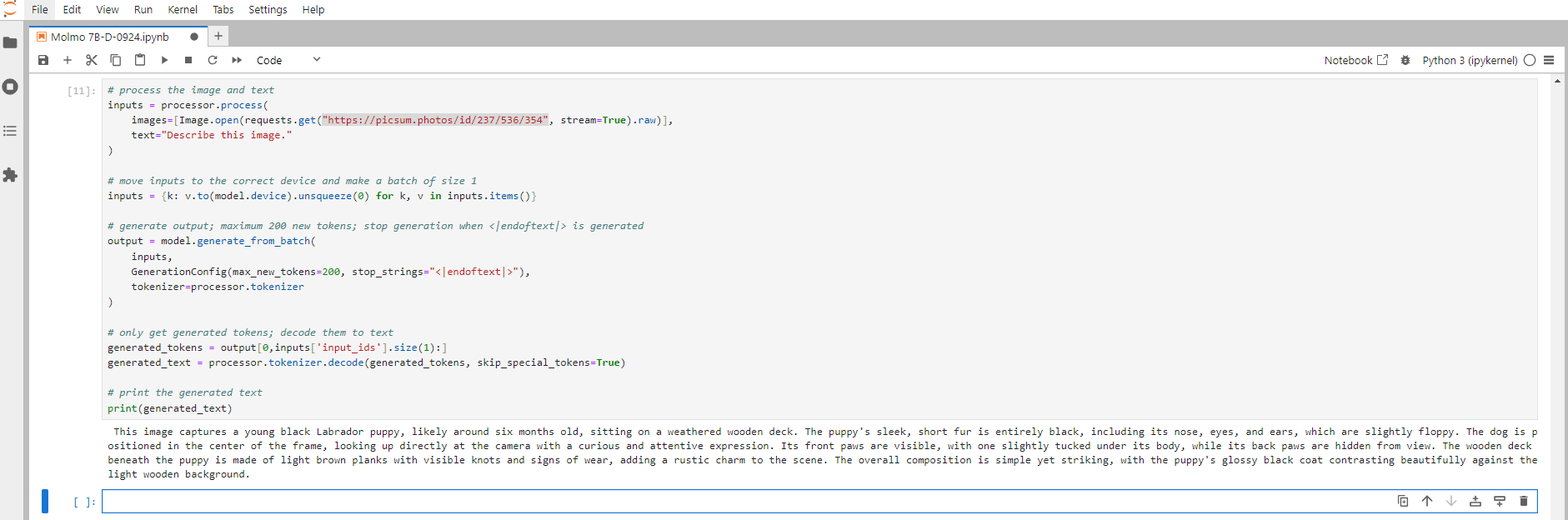
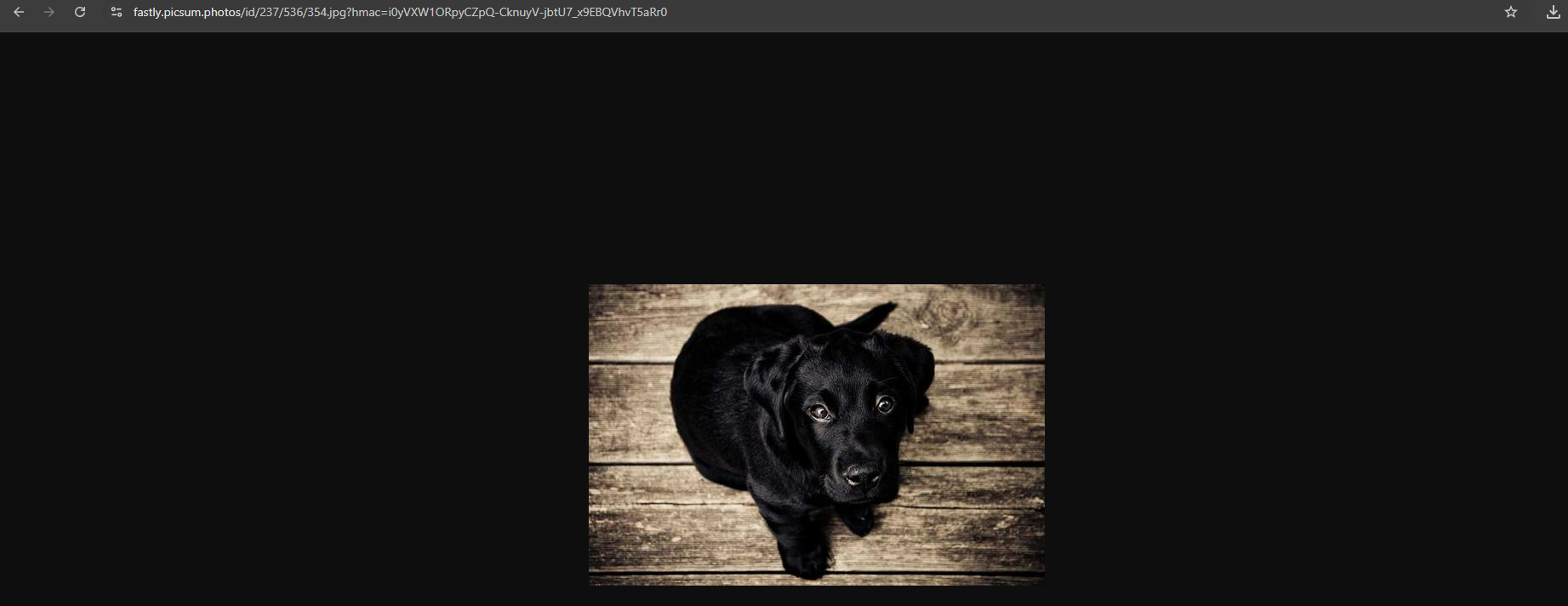
Example 2:
# process the image and text
inputs = processor.process(
images=[Image.open(requests.get("https://picsum.photos/id/237/536/354", stream=True).raw)],
text="Describe this image."
)
# move inputs to the correct device and make a batch of size 1
inputs = {k: v.to(model.device).unsqueeze(0) for k, v in inputs.items()}
# generate output; maximum 200 new tokens; stop generation when <|endoftext|> is generated
output = model.generate_from_batch(
inputs,
GenerationConfig(max_new_tokens=200, stop_strings="<|endoftext|>"),
tokenizer=processor.tokenizer
)
# only get generated tokens; decode them to text
generated_tokens = output[0,inputs['input_ids'].size(1):]
generated_text = processor.tokenizer.decode(generated_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True)
# print the generated text
print(generated_text)
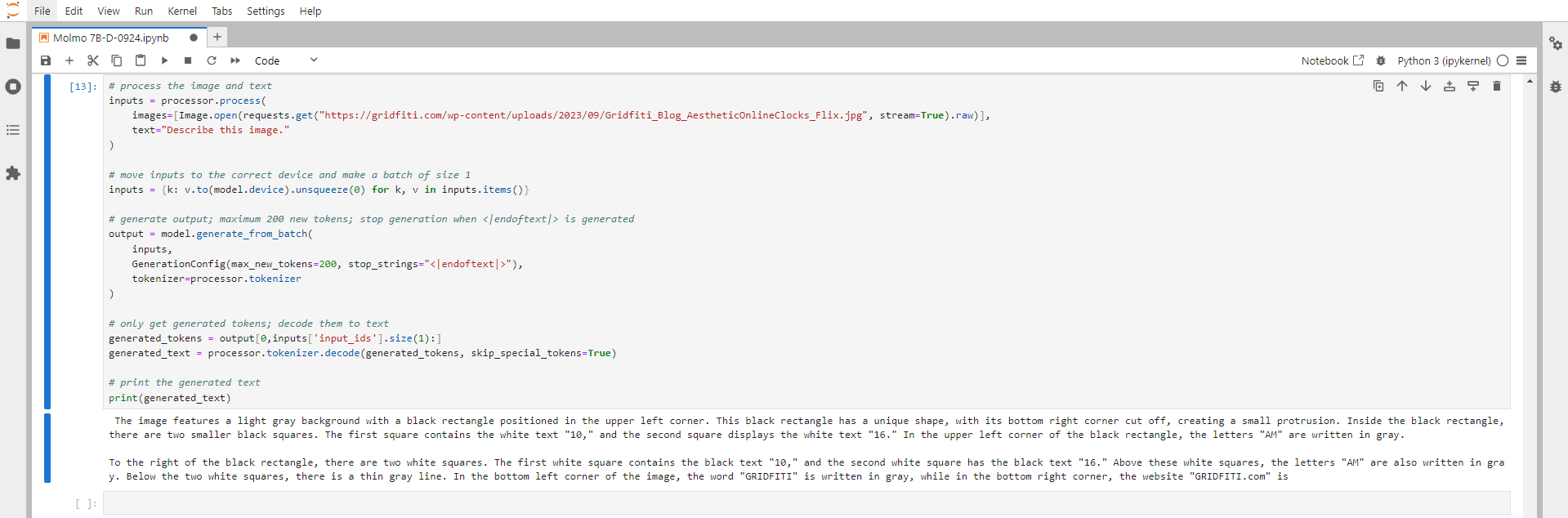
Conclusion
Molmo 7B-D-0924 is a groundbreaking open-source model from Allen Institute for AI that brings state-of-the-art AI capabilities to developers and researchers. Following this guide, you can quickly deploy Molmo 7B-D-0924 on a GPU-powered Virtual Machine with NodeShift, harnessing its full potential. NodeShift provides an accessible, secure, affordable platform to run your AI models efficiently. It is an excellent choice for those experimenting with Molmo 7B-D-0924 and other cutting-edge AI tools.