How to Configure WireGuard VPN in the Cloud

WireGuard is an advanced and modern VPN protocol with powerful cryptography. It is a simple, fast VPN implementation, and although it uses advanced cryptography, it is widely deployed and can be used cross-platform.
WireGuard is significant for a few reasons:
✅ It works very quickly, provides a high level of security.
✅ It is deployed with a few lines of code.
✅ Deployment and debugging are easier in WireGuard VPN protocol because of lightweight nature.
✅ It is a faster, more effective way to protect and transfer data across a VPN.
WireGuard VPN Server Prerequisites
- An account on the NodeShift cloud platform or any cloud provider of your choice.
- A server with a fresh installation of the latest Ubuntu version 22.04, with
sudoprivileges. - A root user account.
- SSH access to the virtual machine.
- Basic knowledge of Linux command-line operations
- Up to 16GB RAM and 4 vCPU, exceeding recommended specifications.
- At least 50GB of SSD storage is recommended, preferably more, depending on your use case.
Step-by-step process to Configure WireGuard VPN on a Cloud Server
For the purpose of this tutorial, we will use a CPU-powered Virtual Machine offered by NodeShift; however, you can replicate the same steps with any other cloud provider of your choice. NodeShift provides the most affordable Virtual Machines at a scale that meets GDPR, SOC2, and ISO27001 requirements.
Step 1: Sign Up and Set Up a NodeShift Cloud Account
- Visit the NodeShift Platform and create an account.
- Once you've signed up, log into your account.
- Follow the account setup process and provide the necessary details and information.
Step 2: Create a Compute Node (CPU Virtual Machine)
NodeShift Compute Nodes offers flexible and scalable on-demand resources like NodeShift Virtual Machines (VMs), which are easily deployed and come with general-purpose, CPU-powered, or storage-optimized nodes.
- Navigate to the menu on the left side.
- Select the "Compute Nodes" option.
- Click the "Create Compute Nodes" button in the Dashboard to make your first deployment.
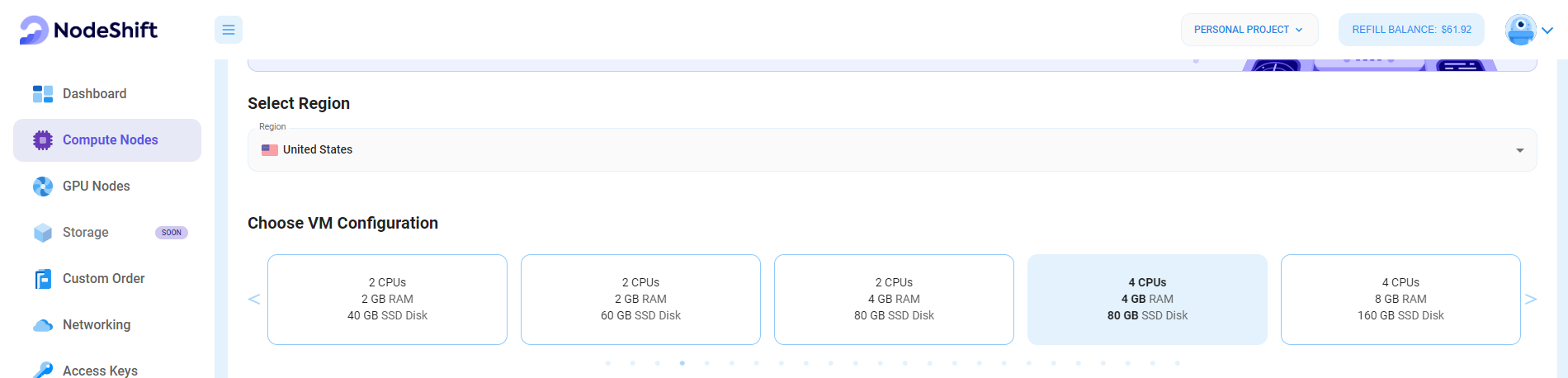
Step 3: Select a Region and Choose VM Configuration
- In the "Compute Nodes" tab, select a geographical region where you want to launch the Virtual Machine (e.g., the United States).
- In the "Choose VM Configuration" section, select the number of cores, amount of memory, boot disk type, and size that best suits your needs.
- You will need at least 16 GB of storage for the server to run smoothly. If you use NodeShift and need more resources, you can always resize to add more CPUs and RAM.
Step 4: Choose an Image
Next, you will need to choose an image for your Virtual Machine. We will deploy the VM on Ubuntu, but you can choose according to your preference. Other options like CentOS and Debian are also available to Configure WireGuard VPN.
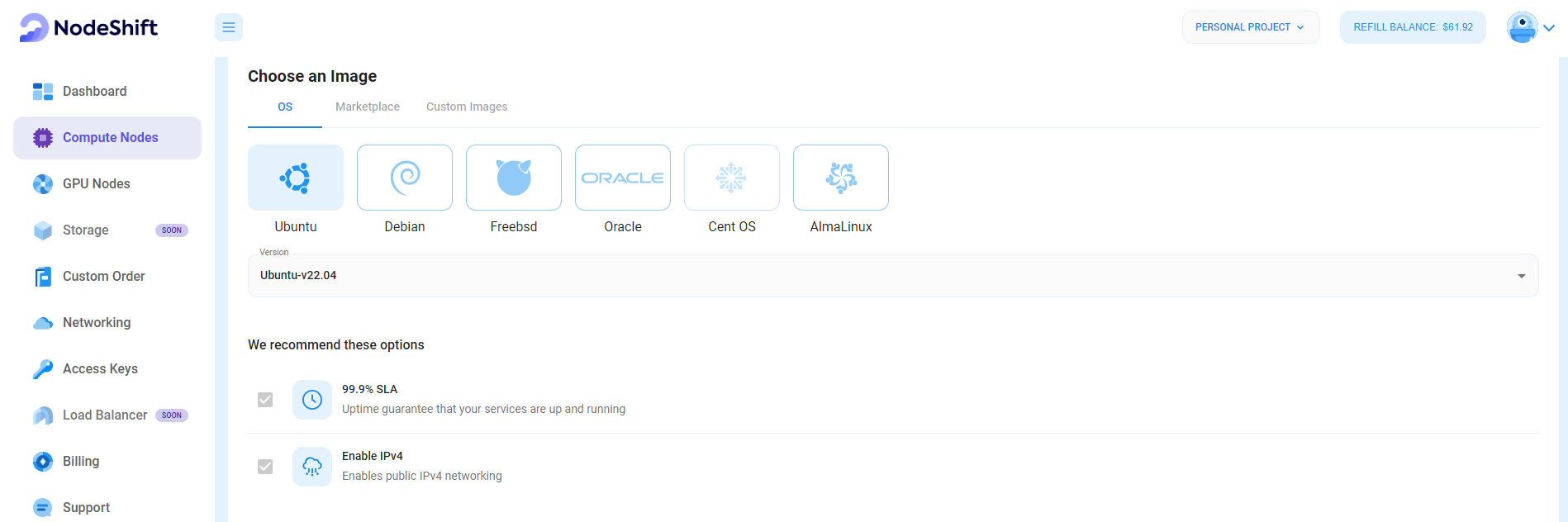
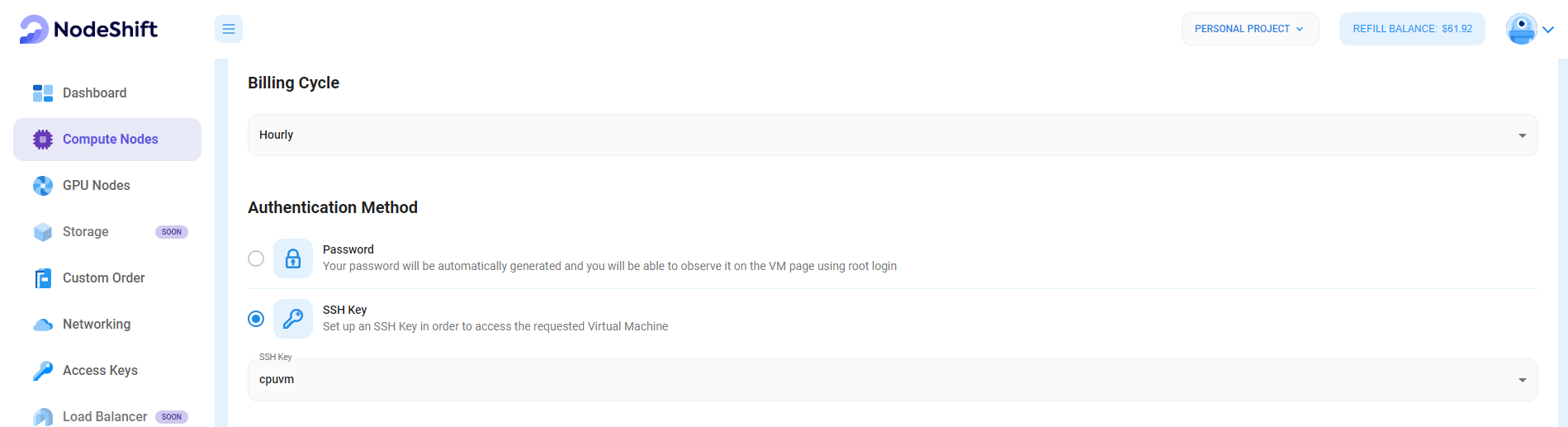
Step 5: Choose the Billing Cycle & Authentication Method
- Select the billing cycle that best suits your needs. Two options are available: Hourly, ideal for short-term usage and pay-as-you-go flexibility, or Monthly, perfect for long-term projects with a consistent usage rate and potentially lower overall cost.
- Select the authentication method. There are two options: Password and SSH Key. SSH keys are a more secure option. To create them, refer to our official documentation.
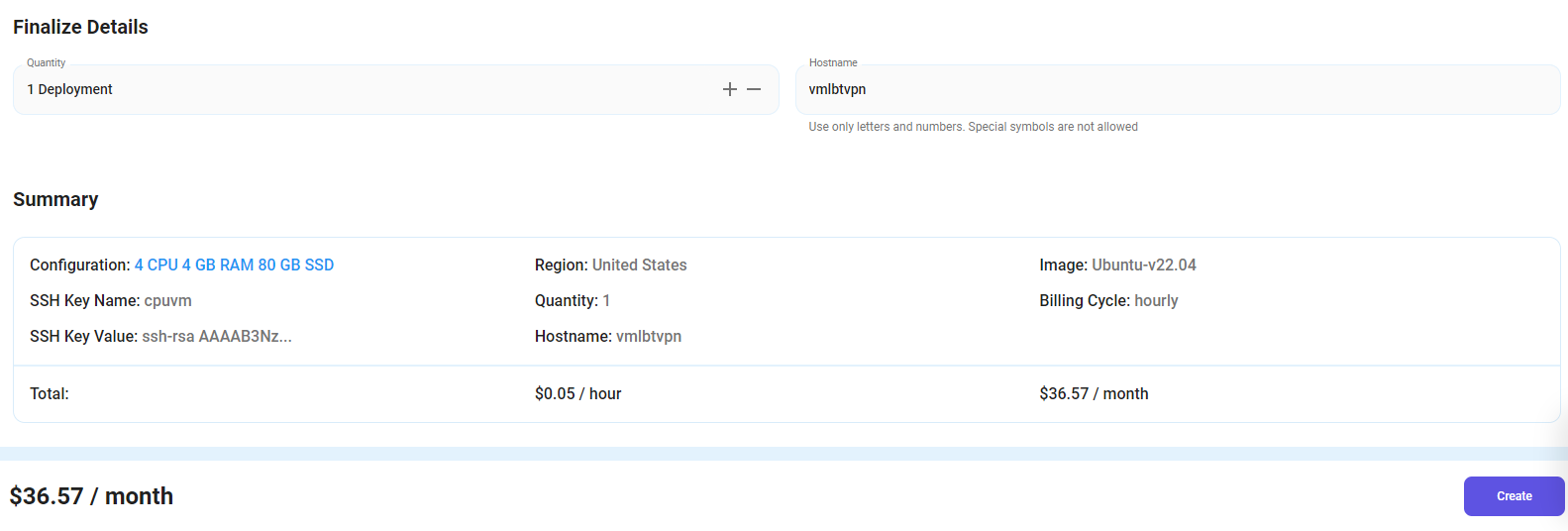
Step 6: Additional Details & Complete Deployment
- The ‘Finalize Details' section allows users to configure the final aspects of the Virtual Machine.
- After finalizing the details, click the 'Create' button, and your Virtual Machine will be deployed.
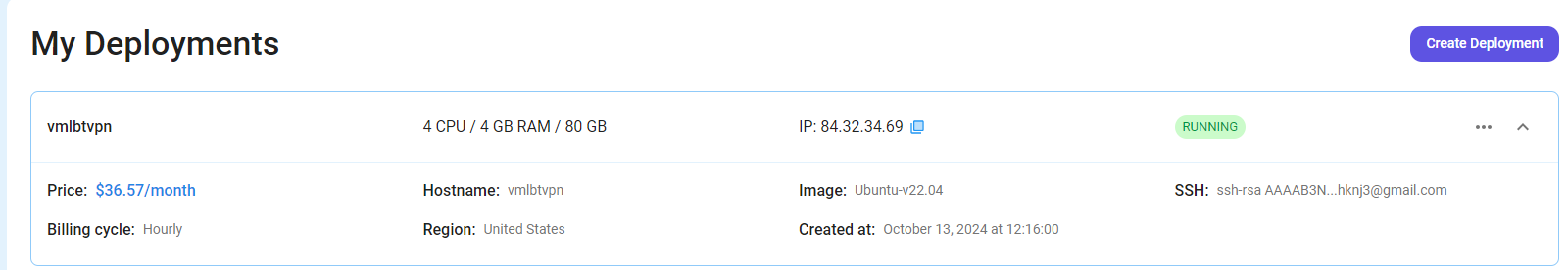
Step 7: Virtual Machine Successfully Deployed
You will get visual confirmation that your node is up and running.
Step 8: Connect via SSH
- Open your terminal
- Run the SSH command:
For example, if your username is root, the command would be:
ssh root@ip
- If SSH keys are set up, the terminal will authenticate using them automatically.
- If prompted for a password, enter the password associated with the username on the VM.
- You should now be connected to your VM!
Step 9: Update your package repository
First, update your package repository. Open a terminal and run the following command:
sudo apt update
Step 10: Install the WireGuard
Run the following command to install WireGuard:
sudo apt install wireguard
Step 11: Generate private and public keys for the server
Run the following commands to generate private and public keys for the server:
wg genkey | sudo tee /etc/wireguard/private.keywg pubkey | sudo tee /etc/wireguard/public.key
Step 12: Update the package list
Before installing any software, we will update the package list using the following command in terminal:
sudo apt update
Step 13: Install Vim
To install Vim, run the following command:
sudo apt install vim -y
This command will retrieve and install Vim and its necessary components.
So, what is Vim?
Vim is a text editor. The last line of the text editor is used to give commands to vim and provide you with information.
Step 14: Create and Enter in Configuration File
Run the following command to create and enter the WireGuard configuration file:
sudo vim /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
Entering the editing mode in Vim:
Follow the below steps to enter the editing mode in Vim
Step 1: Open a File in Vim
Step 2: Navigate to Command Mode
When you open a file in Vim, you start in the command mode. You can issue commands to navigate, save, and manipulate text in this mode. To ensure you are in command mode, press the Esc key. This step is crucial because you cannot edit the text in other modes.
This file contains various settings you can modify, such as PrivateKey, Address, etc.
Add the following configuration in file(adjust IP addresses as needed):
[Interface]
PrivateKey = <server_private_key>
Address = 10.0.0.1/24 # Server's VPN IP address
ListenPort = 51820
[Peer]
PublicKey = <client_public_key>
AllowedIPs = 10.0.0.2/32 # Client's VPN IP addressReplace <server_private_key> with the output from /etc/wireguard/private.key and <client_public_key> key.
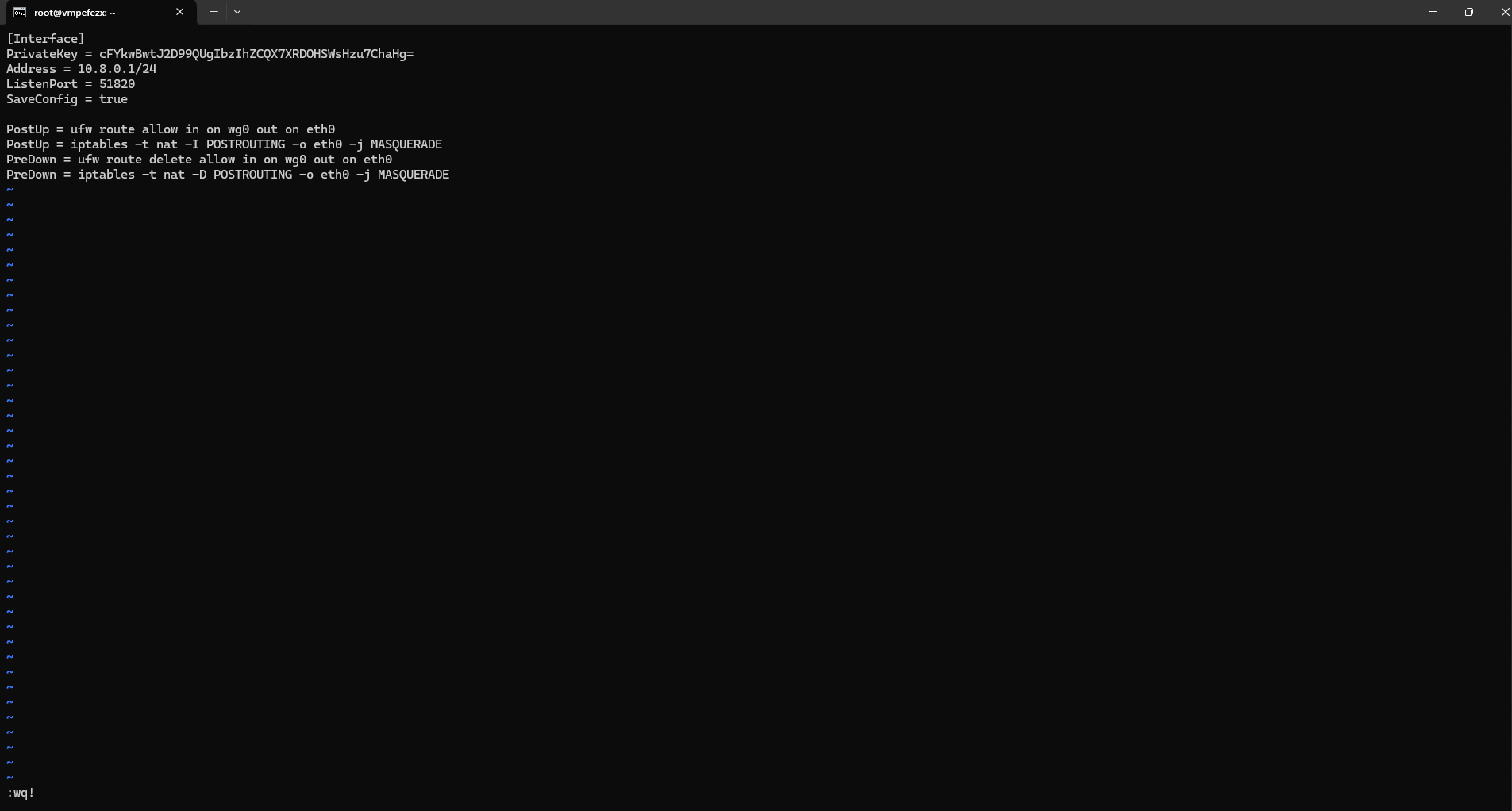
Save and close the file (Ctrl+X, Y, Enter).
Step 15: Configure Network Settings
Run the following command to Enable IP forwarding by editing the sysctl configuration:
sudo vim /etc/sysctl.confThe sysctl file, specifically located at /etc/sysctl.conf, is a configuration file used in Linux-based operating systems to manage kernel parameters at runtime.

Entering the editing mode in Vim:
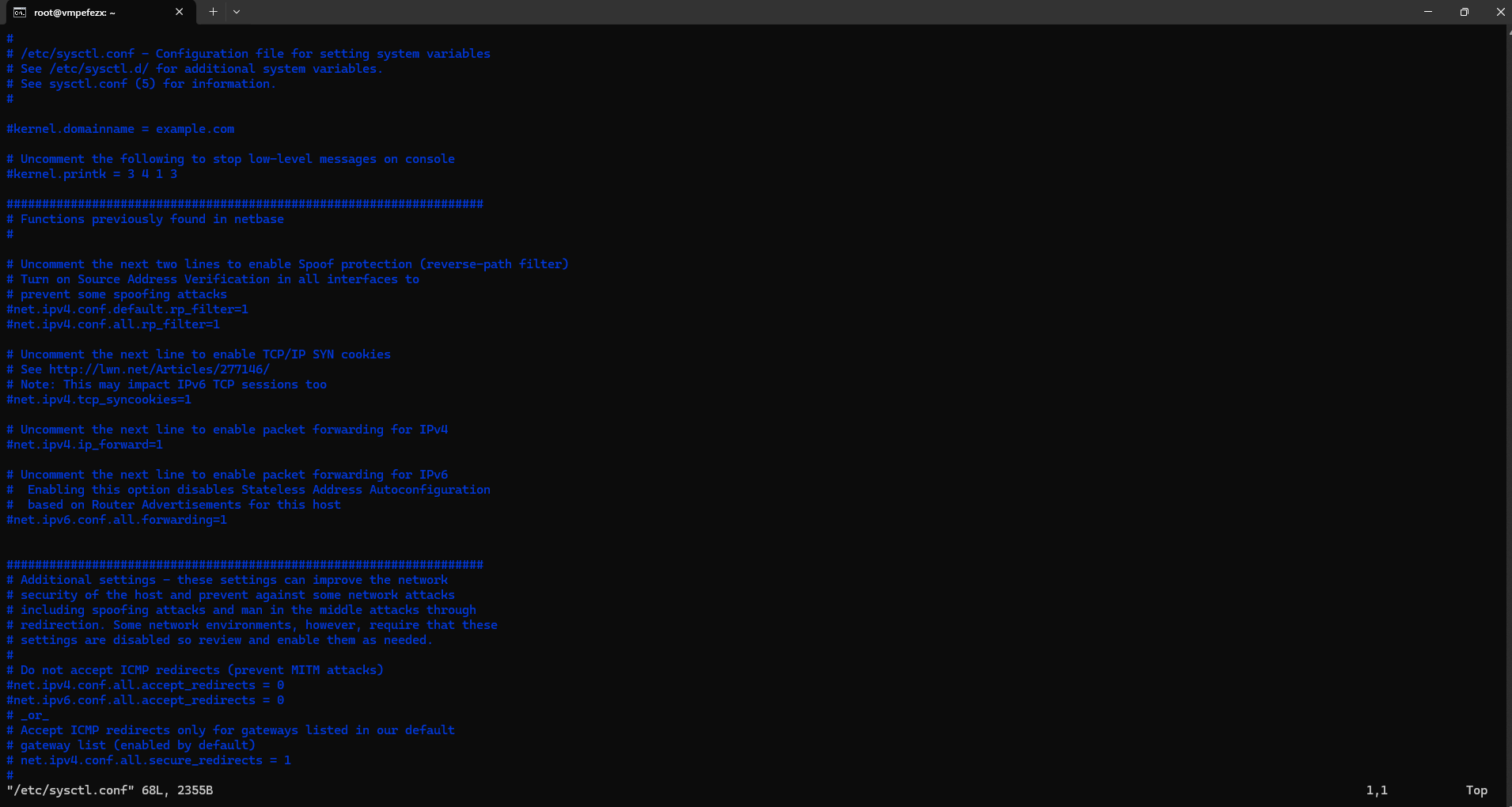
Ensure the following line is uncommented:
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1If this line is not in Vim, then add manually by esc Insert command.
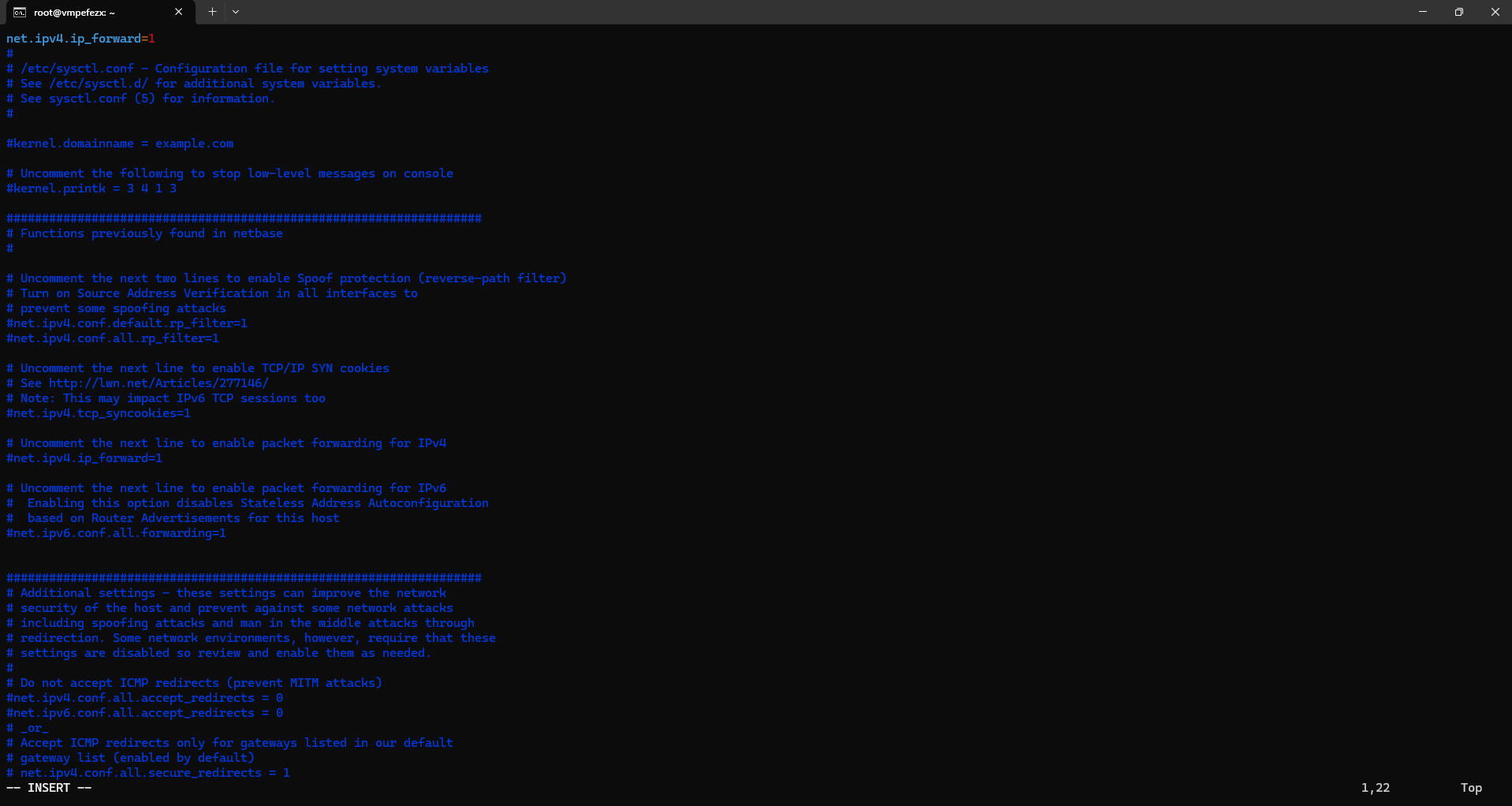
Save and close the file (Ctrl+X, Y, Enter).
Step 16: Apply the changes in sysctl
Run the following command to apply the changes in sysctl:
sudo sysctl -pIf using a firewall (like UFW), allow traffic on the WireGuard port, Run the following command to allow traffic on the WireGuard port:
sudo ufw allow 51820/udp
Step 17: Start WireGuard Service
First run the following command Enable it to start on boot:
sudo systemctl enable wg-quick@wg0.serviceThen, run the following command to Start the WireGuard service:
sudo systemctl start wg-quick@wg0.service Next, run the following command to Monitor the status of the service:
sudo systemctl status wg-quick@wg0.service 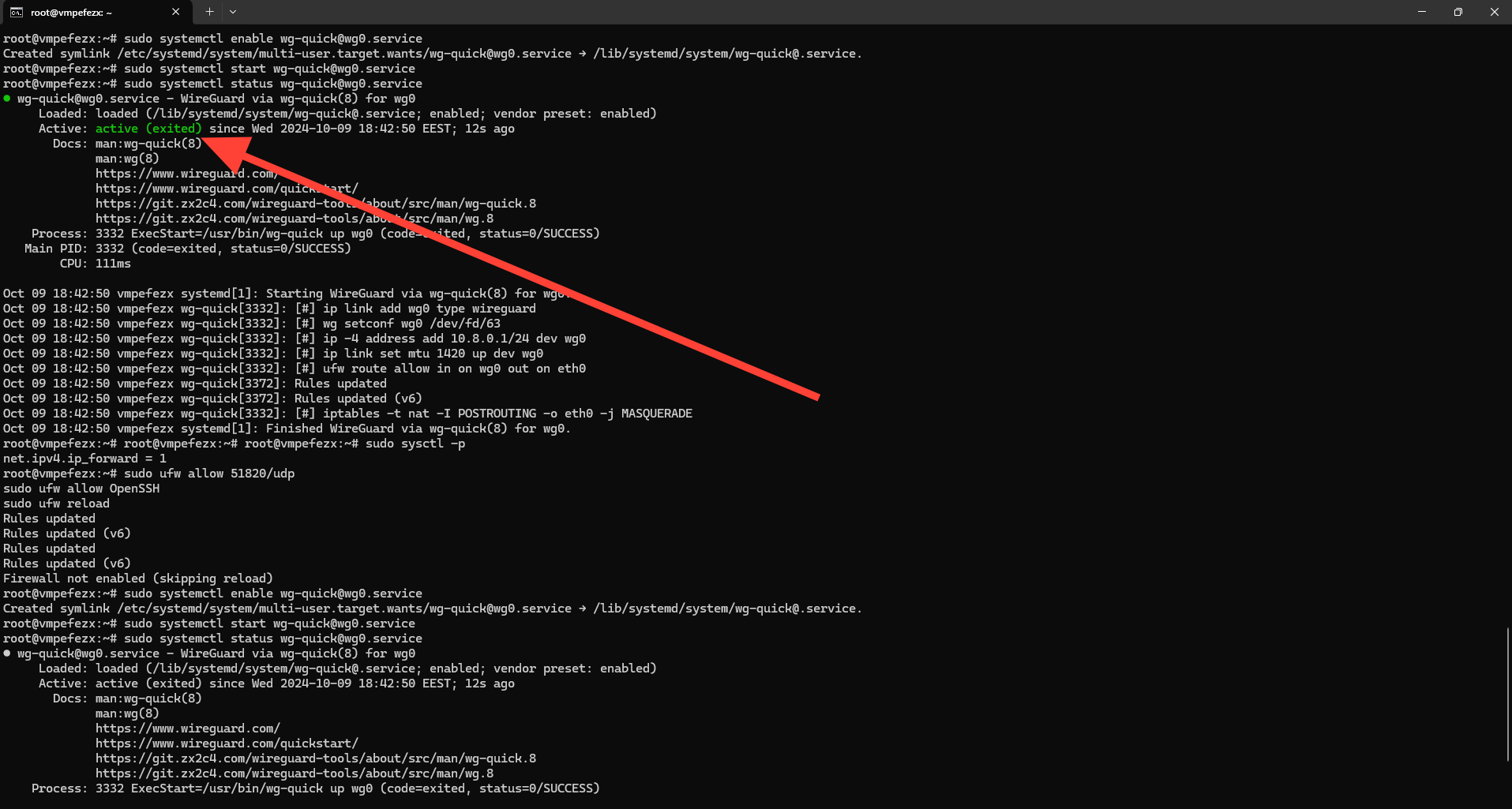
Step 18: Client Configuration(Optional)
On the client device, install WireGuard and generate keys in a similar manner as done on the server. Ensure that the private keys follow the same steps as shown in the screenshots below.

Entering the editing mode in Vim:

Create a client configuration file (e.g., wg-client.conf):
[Interface]
PrivateKey = <client_private_key>
Address = 10.0.0.2/24 # Client's VPN IP address
[Peer]
PublicKey = <server_public_key>
Endpoint = your_server_ip:51820
AllowedIPs = 0.0.0.0/0 # Route all traffic through VPNReplace <client_private_key> and <server_public_key> with the respective keys.
Run the following command to Activate the tunnel on the client:
wg-quick up wg-client.conf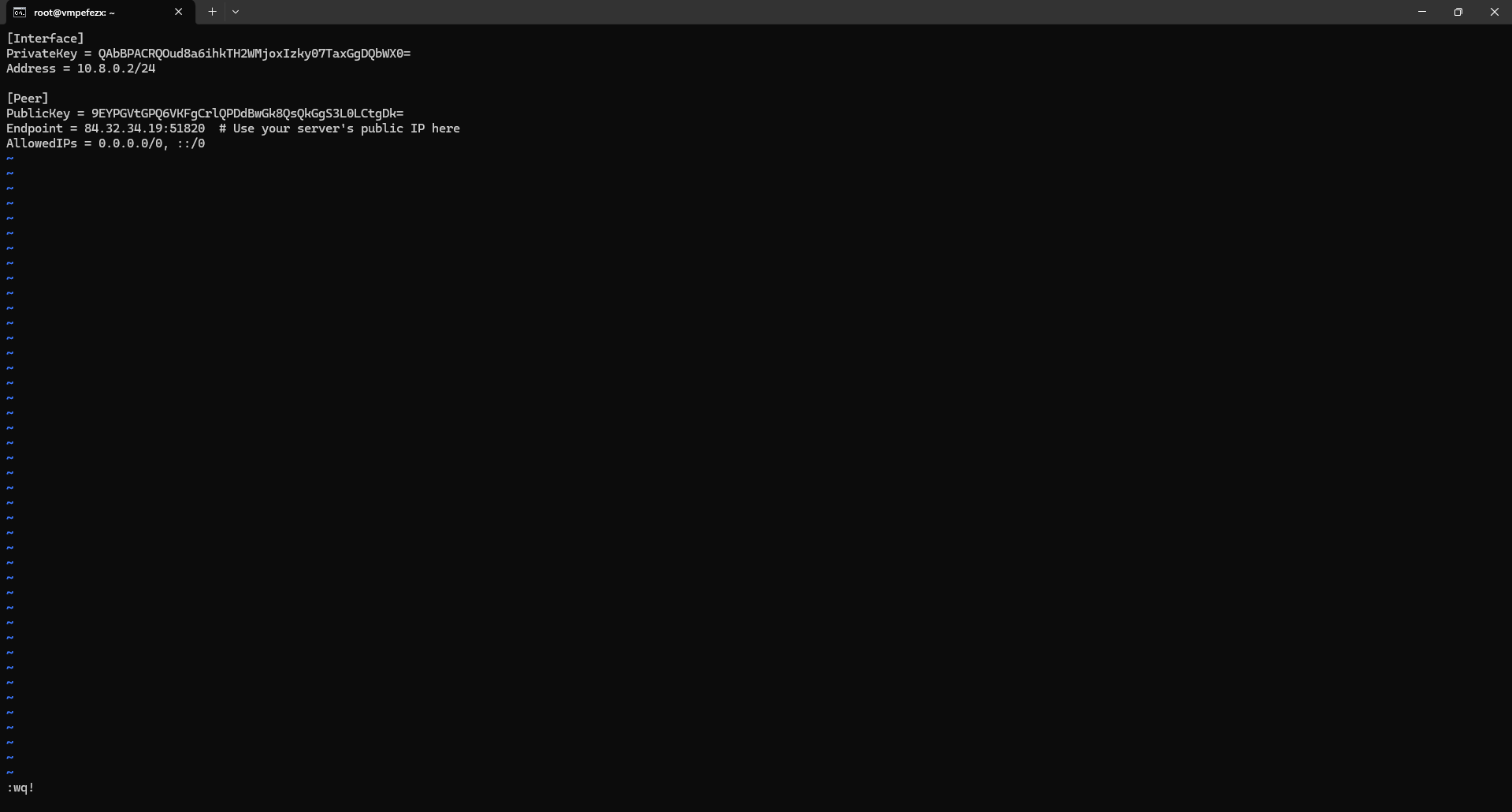
Step 19: Verify Connection
Check if your public IP matches that of your server by visiting a site like https://whatismyipaddress.com. If it matches, your WireGuard VPN is successfully configured.
Conclusion
WireGuard stands out as an excellent choice for those looking to implement a secure and efficient VPN on a Virtual Machine, combining simplicity with high performance and strong security features. By following this step by step guide provides a secure connection through WireGuard, leveraging its efficient protocol and ease of use for both server and client configurations.
For more information about NodeShift: